Spatial Interpolation using three different methods.
Los Angeles County Rainfall calculation
Los Angeles County Rainfall calculation
Introduction
This exercise uses rainfall data from 58 Los Angeles County station for the purpose of creating some interpolated maps of the region about trends in precipitations and its distribution by interpolation of existing data.
The datasets available for rainfall for both current and average normal seasons in Los Angeles County Area are limited to 58 points, which have been manually entered and geographically located through X-Y coordinates definition and taken from the Los Angeles Water Resources Department under "Near real-time precipitation map" (complete list given below at bottom page).
The following list of datasets includes three different methodologies of interpolation analysis, each with different characteristics and quality results, able to give a clear idea of trends and current situation of rainfall for this area. These methods are the IDW method, the Natural Neighbor method and the Kriging method.
The datasets available for rainfall for both current and average normal seasons in Los Angeles County Area are limited to 58 points, which have been manually entered and geographically located through X-Y coordinates definition and taken from the Los Angeles Water Resources Department under "Near real-time precipitation map" (complete list given below at bottom page).
The following list of datasets includes three different methodologies of interpolation analysis, each with different characteristics and quality results, able to give a clear idea of trends and current situation of rainfall for this area. These methods are the IDW method, the Natural Neighbor method and the Kriging method.
Rainfall: Current Season
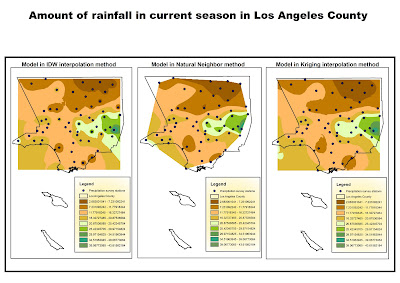 The above map shows the rainfall as in 25th February 2011 for the current season.
The above map shows the rainfall as in 25th February 2011 for the current season.No matters the method used for calculations, it is possible to see how the Eastern
area of the County, corresponding to the Los Angeles Padres Forest, has bigger amounts
of rainfall. This could be related with the fact that many of the stations in that area are located
at higher elevations, where altitude may have influenced amounts of rainfall and then
the amount of vegetation grown in that National Forest. On the other hand, desertic and internal areas have as expected the lesser amounts of rain. There is an augment in coastal areas where micro climates influence rainfall.
The Inverse distance method has as a result a map showing several "islands" of different values
within neighbor limits of those stations having higher values than the rest of the areas more conformal and balanced to the general trends. This can cause several cases of exceptions and gives more weight to the singular records, and so resulting in a map showing several exceptions and a general trend less conform.
The Natural Neighbor method is represented in map two. Here, the trends and the values look shared more equally within all the map, causing less prominence of singular differences compared with the previous map. I think it that in this case, given the fact that the distribution of rainfall within the territory has a simple spatial organization, this is the best of the three methods described for overall three analysis. The fact that one point is closer to a particular station has a strong relationship also in how close is the amount of rainfall to that same station.
Other factors calculated in weighed methods are less precise than this.
Kriging method shows in this case a precision that could be compared with the Natural Neighbor method, and creates Contour lines that are equally shared within the middle-points areas and finally very realistic.
Rainfall: Historic mean of Los Angeles County
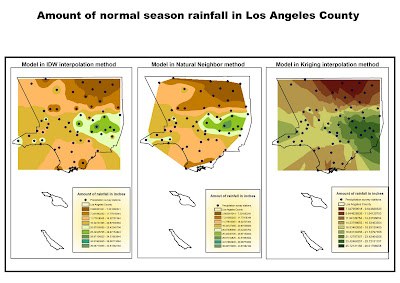 The second map shows the rainfall of a normal season in Los Angeles County. It is inmediately clear that the third case, the Kriging analysis show a map of precipitation substantially different form the other two. This is because in the normal values have been created with a mean calculation process that didn't allow the record of higher peaks of rain in one single station (which have been recorded in more than one case between the current season records).
The second map shows the rainfall of a normal season in Los Angeles County. It is inmediately clear that the third case, the Kriging analysis show a map of precipitation substantially different form the other two. This is because in the normal values have been created with a mean calculation process that didn't allow the record of higher peaks of rain in one single station (which have been recorded in more than one case between the current season records).Kriging analysis had furthermore smoothed and flattened these values, creating a map overall more flattened and with no peaks of value.
By comparing the second maps with the first ones, it is possible to see how rainfall during this current season has been lower than the average historic rainfall. It is possible to recognize also in this case regions where vegetation is more likely to grow and desert areas at North where rainfall is extremely low.
Also in this case, Natural Neighbor Interpolation method produced more equally shared distribution and contour lines of levels of rainfall rather than the Inverse Distance Weighted.
Rainfall: Mapping the Difference within current and historical rainfall
The last map above shows the difference between the current amount of rainfall and the average records for the Los Angeles County area. Blue colors indicate higher rainfall than normal, while Red/Orange values are areas receiving less rain than usual.
Natural Neighbor and IDW methods are methods showing a similar pattern, both indicating as there has been an increase in Western and Southern areas of the County, which correspond to the Los Angeles Padres Forest and the Coastal shoreline between Venice and Long Beach.
Not much has changed instead for the desert areas North of the County. Most of the County however had received much less amounts of rain than expected and probably is affecting reservoirs closer to most urbanized areas. These are in fact located at South-West, where most of the red areas created by the interpolation are located.
In this case, the flattening resulted with the Kraging interpolation method had shared the rainfall more equally within the southern areas and has given probably the most defined map of the differences between the two datasets as a result of the Interpolation.
Natural Neighbor and IDW methods are methods showing a similar pattern, both indicating as there has been an increase in Western and Southern areas of the County, which correspond to the Los Angeles Padres Forest and the Coastal shoreline between Venice and Long Beach.
Not much has changed instead for the desert areas North of the County. Most of the County however had received much less amounts of rain than expected and probably is affecting reservoirs closer to most urbanized areas. These are in fact located at South-West, where most of the red areas created by the interpolation are located.
In this case, the flattening resulted with the Kraging interpolation method had shared the rainfall more equally within the southern areas and has given probably the most defined map of the differences between the two datasets as a result of the Interpolation.
| NAME | ID Number | LAT | LONG | Elevation feet | Current S. | Normal S. | Difference S. | Elevation mts. | |
| Acton Camp Precip | 58 | 34.450556 | -118.198333 | 2,625.00 | 6.65 | 10.03 | -3.38 | 800.10 | |
| Agoura Precip | 56 | 34.135556 | -118.751944 | 800 | 13.7 | 17.84 | -4.14 | 243.84 | |
| Aliso Canyon Precip | 57 | 34.328333 | -118.554722 | 2,367.00 | 20.16 | 22.82 | -2.66 | 721.46 | |
| Aliso Canyon Wagon Wheel | 4 | 34.274722 | -118.526389 | 1112 | 17.13 | 19.57 | -2.44 | 338.94 | |
| Avek Precip | 54 | 34.539167 | -117.923056 | 2,825.00 | 6.06 | 5.78 | 0.28 | 861.06 | |
| Ballona Crk Precip | 55 | 33.998611 | -118.401389 | 38 | 8.94 | 12.39 | -3.45 | 11.58 | |
| Bell Canyon (Rocketdyne) Precip | 52 | 34.178056 | -118.590833 | 2,260.00 | 14.02 | 14.74 | -0.72 | 688.85 | |
| Bell Cyn Debris Basin Precip | 53 | 34.194167 | -118.656389 | 895 | 12.28 | 15.57 | -3.29 | 272.80 | |
| Big Pines Recreation Park Pcp | 50 | 34.378889 | -117.688889 | 6,860.00 | 26.73 | 24.5 | 2.23 | 2,090.93 | |
| Big Rock Mesa Precip | 51 | 34.039167 | -118.616667 | 300 | 19.65 | 16.58 | 3.07 | 91.44 | |
| Big Tujunga-camp15 Precip | 46 | 34.289167 | -118.288056 | 1,525.00 | 13.74 | 19.36 | -5.62 | 464.82 | |
| Bouquet Cyn @ Urban Precip | 47 | 34.448333 | -118.505833 | 1,300.00 | 9.88 | 7.98 | 1.9 | 396.24 | |
| Brand Park Precip | 48 | 34.188056 | -118.271944 | 1,250.00 | 14.17 | 18.34 | -4.17 | 381.00 | |
| Brown's Canyon Precip | 49 | 34.311667 | -118.607222 | 2,400.00 | 19.25 | 19.55 | -0.3 | 731.52 | |
| Cedar Springs Precip | 42 | 34.355833 | -117.873333 | 6,780.00 | 30.16 | 29.95 | 0.21 | 2,066.54 | |
| Chilao-St Hwy Precip | 43 | 34.317778 | -118.008056 | 5,275.00 | 20.75 | 22.9 | -2.15 | 1,607.82 | |
| Clear Crk School Precip | 44 | 34.276944 | -118.17 | 3,150.00 | 27.52 | 30.54 | -3.02 | 960.12 | |
| Cogswell Dam Precip | 45 | 34.243333 | -117.963333 | 2,300.00 | 25.47 | 34.21 | -8.74 | 701.04 | |
| Domin Wat Co Precip | 39 | 33.831389 | -118.224722 | 30 | 13.9 | 12.11 | 1.79 | 9.14 | |
| DP WHQ | 1 | 34.081667 | -118.150278 | 466 | 18.5 | 16.82 | 1.68 | 142.04 | |
| Eagle Rock Rsvr Precip | 40 | 34.145556 | -118.19 | 1,085.00 | 16.34 | 18.14 | -1.8 | 330.71 | |
| Eaton Wash Precip | 41 | 34.074722 | -118.054722 | 261 | 16.26 | 12.4 | 3.86 | 79.55 | |
| Flintridge Precip | 38 | 34.181667 | -118.185556 | 1,600.00 | 23.03 | 22.09 | 0.94 | 487.68 | |
| LA 96th & Cen. Precip | 36 | 33.948889 | -118.254444 | 121 | 12.99 | 13.78 | -0.79 | 36.88 | |
| LA Ducommun St Precip | 37 | 34.0525 | -118.236667 | 306 | 13.54 | 15.63 | -2.09 | 93.27 | |
| La Mirada Precip | 28 | 33.883056 | -118.016667 | 75 | 9.33 | 13.45 | -4.12 | 22.86 | |
| La Rvr @ Wardlow Precip | 29 | 33.819722 | -118.122 | 25 | 11.3 | 9.9 | 1.4 | 7.62 | |
| La Tuna DB Precip | 30 | 34.236667 | -118.326667 | 1,160.00 | 12.52 | 16.44 | -3.92 | 353.57 | |
| Lancaster Roper Precip | 31 | 34.679722 | -118.010278 | 2,400.00 | 7.24 | 5.34 | 1.9 | 731.52 | |
| Lancaster Waterworks | 3 | 34.801111 | -118.559722 | 2910 | 7.24 | 5.34 | 1.9 | 886.97 | |
| Le Habra Heights | 11 | 33.960833 | -117.950556 | 755 | 15.98 | 15.85 | 0.13 | 230.12 | |
| Lechuza Pat Sta Precip | 32 | 34.076944 | -118.879444 | 1,620.00 | 21.85 | 22.4 | -0.55 | 493.78 | |
| Lewis Ranch Precip | 33 | 34.42 | -117.886389 | 4,615.00 | 17.17 | 15.21 | 1.96 | 1,406.65 | |
| Little Gleason Precip | 34 | 34.378333 | -118.149167 | 5,600.00 | 15.67 | 23.87 | -8.2 | 1,706.88 | |
| Little Rock Crk Above Dam Percip | 35 | 34.478056 | -118.023333 | 3,267.00 | 9.8 | 9.16 | 0.64 | 995.78 | |
| Loomis Ranch Precip | 27 | 34.348333 | -118.048056 | 4,325.00 | 15.39 | 18.55 | -3.16 | 1,318.26 | |
| Mescal Smith Precip | 24 | 34.4675 | -117.711111 | 3,810.00 | 9.29 | 7.8 | 1.49 | 1,161.29 | |
| Mint Cyn @ Fitch Precip | 25 | 34.446667 | -118.4275 | 1,652.00 | 9.02 | 9.05 | -0.03 | 503.53 | |
| Monte Nido Fire Precip | 26 | 34.077778 | -118.692222 | 600 | 19.65 | 22 | -2.35 | 182.88 | |
| Newhall-Sol Precip | 21 | 34.425833 | -118.578333 | 1,243.00 | 13.74 | 17.89 | -4.15 | 378.87 | |
| North Lancaster Precip | 22 | 34.761389 | -118.125 | 2,310.00 | 2.68 | 5.19 | -2.51 | 704.09 | |
| Northridge- LADPW Precip | 23 | 34.231111 | -118.541111 | 1,117.00 | 12.8 | 15.3 | -2.5 | 340.46 | |
| Pacoima Dam Precip | 20 | 34.33 | -118.399444 | 1,950.00 | 17.2 | 19.54 | -2.34 | 594.36 | |
| Palmdale Water Dist Precip | 17 | 34.594722 | -118.091944 | 2,595.00 | 7.17 | 6.93 | 0.24 | 790.96 | |
| Pine Canyon Patrol Station Pcp | 18 | 34.673333 | -118.429167 | 3,286.00 | 17.24 | 19.14 | -1.9 | 1,001.57 | |
| Pnt Vicen Ligh Precip | 19 | 33.741667 | -118.410556 | 125 | 18.87 | 11.07 | 7.8 | 38.10 | |
| Pudd Div Precip | 15 | 34.129167 | -117.780833 | 1,130.00 | 20.43 | 19.21 | 1.22 | 344.42 | |
| Quartz Hill Precip | 16 | 34.648056 | -118.24 | 2,395.00 | 9.96 | 7.97 | 1.99 | 730.00 | |
| Redman Precip | 14 | 34.764444 | -117.925 | 2,360.00 | 5.59 | 5.18 | 0.41 | 719.33 | |
| Relay | 2 | 34.735 | -117.776944 | 3057 | 6.52 | 5.15 | 1.37 | 931.77 | |
| Rocky Buttes Precip | 13 | 34.65 | -117.863333 | 2,540.00 | 6.57 | 4.84 | 1.73 | 774.19 | |
| San Gab Pow House Precip | 12 | 34.155556 | -117.907778 | 744 | 16.16 | 22.98 | -6.82 | 226.77 | |
| San Gabriel Dam Precip | 7 | 34.205556 | -117.860556 | 1,481.00 | 28.78 | 28.86 | -0.08 | 451.41 | |
| San Gabriel East Fork Percip | 8 | 34.235833 | -117.805 | 1,600.00 | 25.55 | 26.04 | -0.49 | 487.68 | |
| Sanberg Airways Station Precip | 9 | 34.746389 | -118.724167 | 3,635.00 | 10.94 | 12.85 | -1.91 | 1,107.95 | |
| Santa Anita Dam Precip | 10 | 34.184167 | -118.019722 | 1,400.00 | 27.17 | 26.21 | 0.96 | 426.72 | |
| Tanbark Precip | 6 | 34.205278 | -117.760833 | 2,750.00 | 43.66 | 28.04 | 15.62 | 838.20 | |
| Topanga Canyon Patrol Station Pcp | 5 | 34.084167 | -118.599167 | 745 | 18.89 | 24.42 | -5.53 | 227.08 |

No comments:
Post a Comment